Applications
You can use Application support to graph performance statistics of many applications.
Different applications support a variety of ways to collect data:
- By direct connection to the application
- snmpd extend
- The agent.
The monitoring of applications could be added before or after the hosts have been added to LibreNMS.
If multiple methods of collection are listed you only need to enable one.
SNMP Extend
When using the snmp extend method, the application discovery module will pick up which applications you have set up for monitoring automatically, even if the device is already in LibreNMS. The application discovery module is enabled by default for most *nix operating systems, but in some cases you will need to manually enable the application discovery module.
SUDO
One major thing to keep in mind when using SNMP extend is these run as the snmpd user that can be an unprivileged user. In these situations you need to use sudo.
To test if you need sudo, first check the user snmpd is running as. Then test if you can run the extend script as that user without issue.
Example
If snmpd is running as Debian-snmp and we want to run the extend for proxmox, we check that the following run without error:
sudo -u Debian-snmp /usr/local/bin/proxmox
If it doesn't work, then you will need to use sudo with the extend command. For the example above, that would mean adding the line below to the sudoers file:
Debian-snmp ALL = NOPASSWD: /usr/local/bin/proxmox
Finally we would need to add sudo to the extend command, which would look like that for proxmox:
extend proxmox /usr/bin/sudo /usr/local/bin/proxmox
Restart snmpd
sudo systemctl restart snmpd
sudo service snmpd restart
JSON Return Optimization Using librenms_return_optimizer
While the json_app_get does allow for more complex and larger data to be easily returned by a extend and the data to then be worked with, this can also sometimes result in large returns that occasionally don't play nice with SNMP on some networks.
librenms_return_optimizer fixes this via taking the extend output piped to it, gzipping it, and then converting it to base64. The later is needed as net-snmp does not play that nice with binary data, converting most of the non-printable characters to .. This does add a bit of additional overhead to the gzipped data, but still tends to be result in a return that is usually a third of the size for JSONs items.
The change required is fairly simply. So for the portactivity example below...
extend portactivity /etc/snmp/extends/portactivity smtps,http,imap,imaps,postgresql,https,ldap,ldaps,nfsd,syslog-conn,ssh,matrix,gitea
Would become this...
extend portactivity /usr/local/bin/lnms_return_optimizer -- /etc/snmp/extends/portactivity smtps,http,imap,imaps,postgresql,https,ldap,ldaps,nfsd,syslog-conn,ssh,matrix,gitea
The requirements for this are Perl, MIME::Base64, and Gzip::Faster.
pkg install p5-MIME-Base64 p5-Gzip-Faster wget
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/librenms/librenms-agent/master/utils/librenms_return_optimizer -O /usr/local/bin/librenms_return_optimizer
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/librenms_return_optimizer
apt-get install zlib1g-dev cpanminus wget
cpanm Gzip::Faster
cpanm MIME::Base64
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/librenms/librenms-agent/master/utils/librenms_return_optimizer -O /usr/local/bin/librenms_return_optimizer
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/librenms_return_optimizer
yum install zlib-devel perl-CPAN wget
cpan Gzip::Faster
cpan MIME::Base64
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/librenms/librenms-agent/master/utils/librenms_return_optimizer -O /usr/local/bin/librenms_return_optimizer
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/librenms_return_optimizer
Currently supported applications as are below.
- backupninja
- certificate
- chronyd
- dhcp-stats
- docker
- fail2ban
- fbsd-nfs-client
- fbsd-nfs-server
- gpsd
- mailcow-postfix
- mdadm
- ntp-client
- ntp-server
- portactivity
- powerdns
- powermon
- puppet-agent
- pureftpd
- redis
- seafile
- supervisord
- ups-apcups
- zfs
The following apps have extends that have native support for this, if congiured to do so.
- suricata
Enable the application discovery module
- Edit the device for which you want to add this support
- Click on the Modules tab and enable the
applicationsmodule. - This will be automatically saved, and you should get a green confirmation pop-up message.
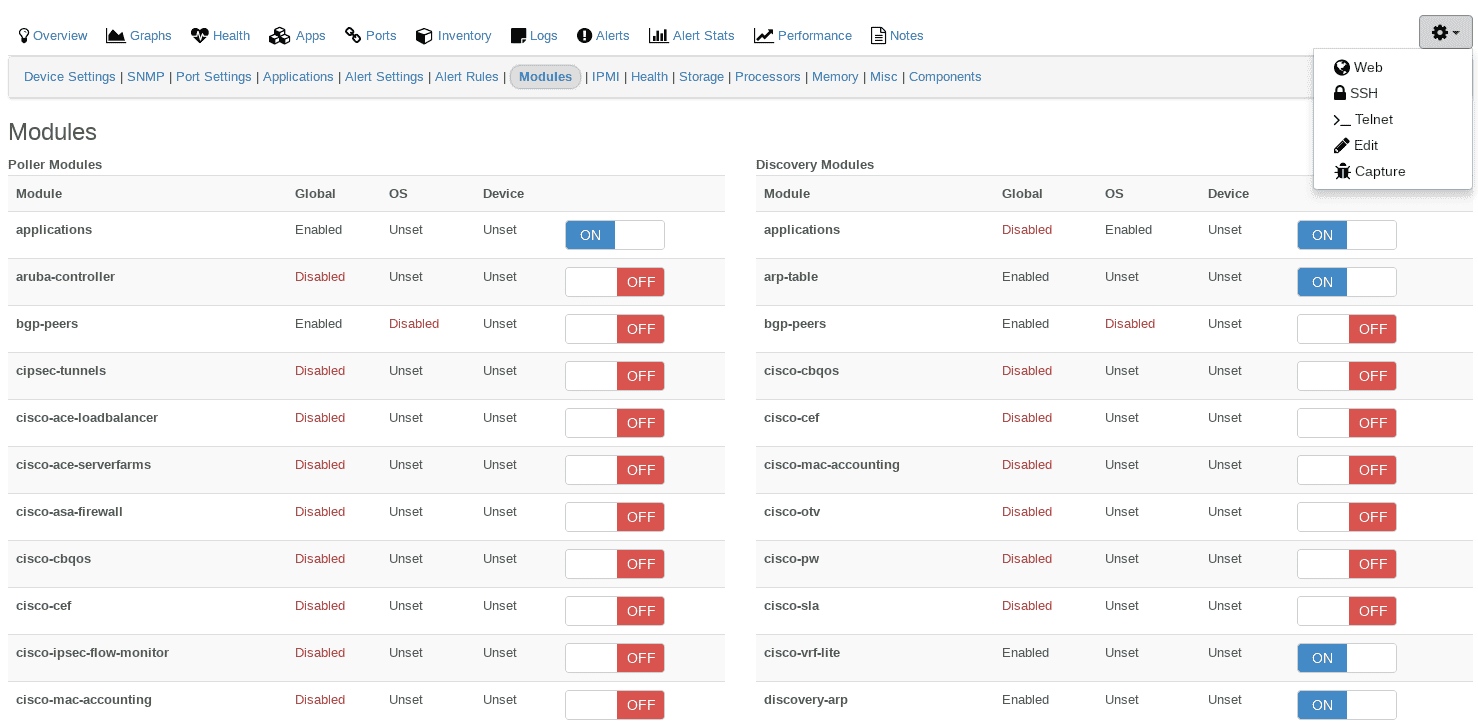
After you have enabled the application module, it would be wise to then also enable which applications you want to monitor, in the rare case where LibreNMS does not automatically detect it.
Note: Only do this if an application was not auto-discovered by LibreNMS during discovery and polling.
Enable the application(s) to be discovered
- Go to the device you have just enabled the application module for.
- Click on the Applications tab and select the applications you want to monitor.
- This will also be automatically saved, and you should get a green confirmation pop-up message.
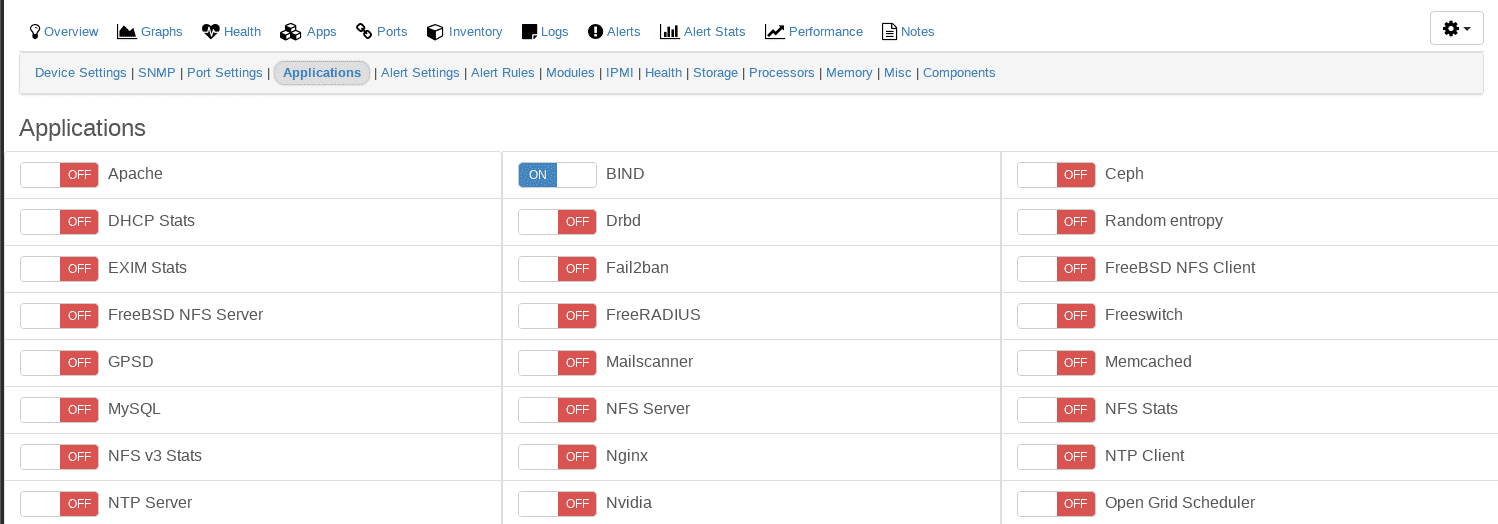
Agent
The unix-agent does not have a discovery module, only a poller module. That poller module is always disabled by default. It needs to be manually enabled if using the agent. Some applications will be automatically enabled by the unix-agent poller module. It is better to ensure that your application is enabled for monitoring. You can check by following the steps under the SNMP Extend heading.